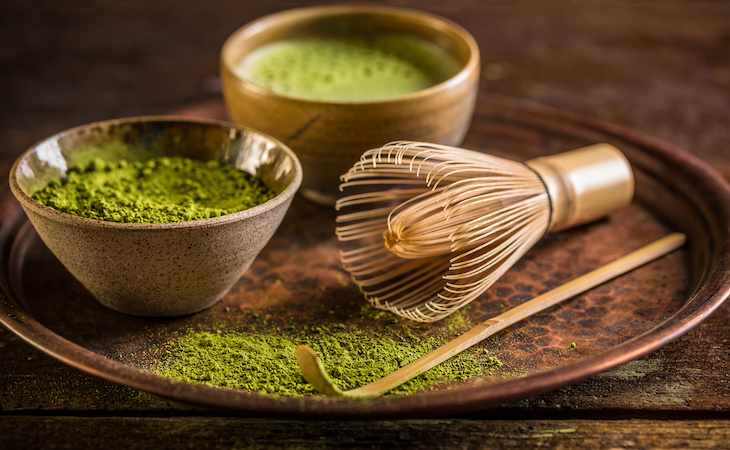
Green, black, and white teas are consumed worldwide today—but more recently, matcha tea, a green tea, has earned a reputation as the highest quality tea because of its functional ingredients, nutritional makeup, and naturally sweet earthy flavors.
Research published in the journal Current Research in Food Science shows that matcha lowers stress and anxiety levels and slightly improves memory and attention. With a third of US adults struggling to get enough sleep, some may turn to tea for better shuteye.
Is matcha good for sleep? See why many people are going green with matcha and whether to add it to your slumber routine.
What is matcha?
You’ve probably seen matcha’s eye-catching bright green hues displayed in smoothies, lattes, cookies, cakes, mochi, and many other foods and drinks. In the 1100s, a Buddhist monk introduced matcha to Japan, which comes from the leaves of the Camellia sinensis plant.
Unlike traditional teas, matcha is uniquely made from powdered tea leaves, so the whole leaf is ingested. If you’re a beginner to tea, it helps to know that many tea types are extracted from soaked leaves. But, in making matcha, the tea leaves are steamed, deveined, and finely ground.
How does matcha work?
Matcha is packed with a wide range of potent compounds responsible for its beneficial effects on health. Here are the top compounds in matcha tea.
- Catechins: Matcha is rich in catechins, a group of four major compounds with high antioxidant functions. EGCG is a type of catechin most abundant in matcha and many other green tea types.
- Caffeine: Caffeine works as an antioxidant that may offer anti-inflammatory effects. Compared to other green teas, matcha has a higher caffeine content, which adds to its unique flavor and smell.
- Phenolic acids: Phenolic acids may sound intimidating, but they’re plant compounds with many health benefits. Gallic acid, ellagic acid, and chlorogenic acid are phenolic acids found in matcha and are known for anticancer, anti-inflammatory, and antibacterial protective benefits.
- Rutin: Matcha tea may be one of the richest sources of rutin, an antioxidant. Rutin is important because it works synergistically with vitamin C and may enhance how both work in the cardiovascular system, according to a study in Foods. Rutin may also protect against diabetes.
- Quercetin: Another plant chemical and antioxidant, quercetin may help protect brain health and may help with blood sugar balance. Matcha’s quercetin content is also higher than regular green tea.
- Vitamin C: Vitamin C is an essential antioxidant your body can’t make, so ingesting it through foods and drinks like matcha is crucial.
- Chlorophyll: Matcha’s vibrant green color is owed to its chlorophyll contents, which offer powerful anti-inflammatory and antioxidant benefits, according to Food Chemistry.
- L-theanine: Theanine is an amino acid responsible for matcha’s unique umami flavor. Combined with caffeine, the duo may do a better job of improving focus, attentiveness, and relieving stress than on their own.
The health and sleep benefits of matcha
It’s abundant in antioxidants to fight diseases
Oxidants, including reactive oxygen species (ROS) and free radicals, form inside your body naturally. Excess oxidants can lead to oxidative stress and inflammation, which can also happen with sleep loss.
Antioxidants in matcha tea can clear oxidants for optimal health and disease prevention. Matcha has twice as much vitamin C as traditional green tea, which may help with immune health.
It may help improve heart health
Matcha has stopped weight gain, reduced cholesterol, and improved blood sugar levels in animal studies. EGCG may improve fat breakdown, which could impact body weight and heart health.
Moreover, theanine ingestion might assist in lower blood pressure and less inflammation, which could lower the chances of cardiac and metabolic disease.
It could enhance brain function and lower anxiety
According to a review in Current Research in Food Science, multiple studies found caffeine to increase alertness and improve brain performance. Additionally, matcha is loaded with polyphenols, active compounds that readily cross the blood-brain barrier, exerting brain protection. Its other brain-boosting ingredient, theanine, also may help your attention span.
Further, a small study in Nutrients looked at matcha’s effect on stress and anxiety, and they gave 39 students 3 grams of matcha or a placebo to drink every day for 15 days. The study found significantly lower anxiety and stress levels compared to placebo.
It might win you better sleep
According to a Plant Foods for Human Nutrition study, theanine may offer sleep-enhancing perks, including improving mood and lessening stress and anxiety. Structurally, theanine looks like an excitatory neurotransmitter called glutamate, and it may block glutamate receptors in the central nervous system, promoting a calming effect.
Additionally, theanine could improve sleep disturbances and enhance non-rapid eye movement (NREM) sleep by promoting relaxation through the enhancement of GABA levels. GABA is a neurotransmitter that raises serotonin, a sleep regulator. Remember, matcha’s caffeine can disrupt sleep, but there are ways to preserve your sleep habits with matcha.
How to use matcha to improve your sleep
- Consider its caffeine content: A study in Nutrients found that drinking low-caffeine green teas was linked to higher-quality sleep, even after being consumed in high amounts. Teas were consumed in the mornings and evenings. Your safest bet to reap the many health benefits of matcha tea without derailing your sleep may be to enjoy your cup before 3 p.m. if it’s a higher-caffeine matcha. Opt for a low-caffeine matcha if you like sipping tea later in the day.
- Combine matcha with other sleep-promoting ingredients: Consider trying this delicious Ginger Matcha Latte recipe that uses milk, a drink that may help you sleep better. Use a low-caffeine matcha when drinking this in the evenings.
- Listen to your body: If you’ve added matcha into your day or evening routine, pay attention to any changes to your sleep and adjust how much you drink, when you drink, or the caffeine content as needed.
FAQs
Does matcha keep you up at night?
Everyone’s body is different; some may be more sensitive to caffeine than others. Matcha teas have a range of caffeine depending on how they’re made. Drinking matcha tea close to bedtime can delay your slumber since caffeine is a known stimulant that stays in your system for five to six hours.
Is matcha helpful to sleep?
Matcha is rich in L-theanine, an amino acid that may boost mood while helping with relaxation, alleviating stress, and promoting calm, which may help sleep. Contrastingly, matcha’s caffeine can disrupt sleep. To reap its benefits without hindering your sleep, it helps to consider its caffeine content and the right time to enjoy it in your daily routine.
Is matcha better than coffee for insomnia?
Matcha may be a better option for improving sleep because it’s naturally lower in caffeine than coffee. If you struggle with insomnia, it could help to drink caffeinated beverages before 3 p.m. or opt for a caffeine-free beverage, like chamomile, at nighttime.
The bottom line: Many studies on matcha, green tea, and health benefits have small sample sizes or are animal studies. More studies are needed to confirm if matcha is truly good for improved snoozing.
Hungry before bed? Here’s a list of late-night snacks that won’t ruin your sleep.