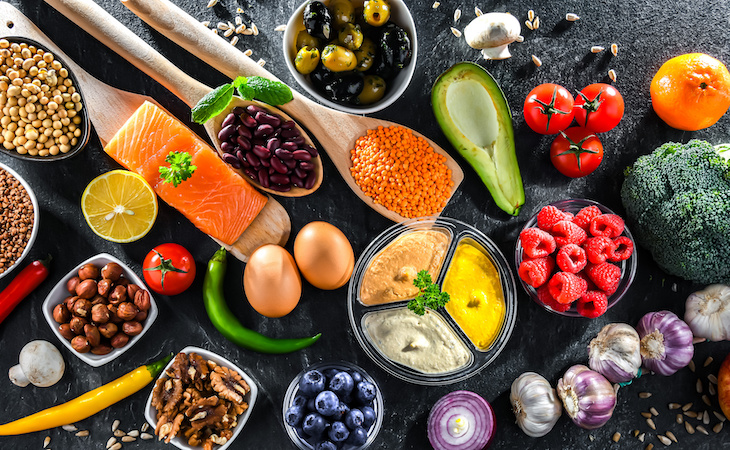
Time and time again, there’s one eating approach that’s consistently thought to be the healthiest diet in the world: the Mediterranean diet.
It’s rich in fruits, vegetables, nuts, whole grains, and legumes. This means it’s an eating plan that’s low in saturated fats, high in heart-healthy fats, and high in fiber. It’s often used in the context of reducing or preventing cardiovascular disease, which is the leading cause of death globally.
With so many health benefits to its name, that made us wonder—could following the Mediterranean diet also improve sleep? Ahead, we’ll explore this possibility.
What is the Mediterranean diet?
“The Mediterranean diet is a style of eating that is supposed to be based on whole or minimally processed foods,” says Michelle Yates, RD, licensed medical nutrition therapist.
There’s no specific definition or strict guidelines for this diet. “Rather, it represents an emphasis on eating high amounts of fruits, vegetables, legumes, whole grains, nuts, seeds, and heart-healthy oils; frequent amounts of fish; moderate amounts of dairy products; low amounts of sweets and red meats/meat products; and wine in moderation,” explains Yates.
The Mediterranean diet has been long thought to be ideal for preventing and reducing symptoms of noncommunicable diseases, such as heart disease, diabetes, cancer, and cognitive impairment-related conditions, adds Yates.
“The Mediterranean diet is a style of eating that is supposed to be based on whole or minimally processed foods.”
Michelle Yates, RD, licensed medical nutrition therapist
The Mediterranean diet emphasizes that all meals should be based on fruits, vegetables, mostly whole grains, beans, nuts, legumes, seeds, herbs, and/or spices.
After the base of the meal is established, fish and seafood are the most typical sources of protein to be added, says Yates. Poultry, eggs, cheese, and yogurt are to be consumed moderately, and red meats and sweets are to be consumed less often.
Additionally, the Mediterranean diet can encourage lifestyle habits like being physically active and enjoying meals with others, says Yates.
Mediterranean diet benefits and risks
When it comes to Mediterranean diet benefits, improved health tops the list, says Yates. Benefits include lower LDLs (bad cholesterol) and higher HDLs (good cholesterol), lower blood pressure, reduced risk of colorectal, breast, prostate, pancreas, and endometrial cancer, better glucose regulation, and improved cognition.
But she cautions that there are risks with following any kind of diet.
“Following a diet always has the potential for someone to follow it too strictly and feel that they are never able to go ‘off plan,’ to the point of sacrificing their social life or the ability for them to be spontaneous,” says Yates. “This can develop into eating disorders/disordered eating (including binge eating episodes when the dieter is fatigued by the diet and wants a release).”
For those who already struggle with disordered eating or are prone to an eating disorder, following a diet can prompt them to develop a full-fledged clinical problem with food, says Yates.
She also points out that many people think the Mediterranean diet is automatically the healthiest diet given the benefits associated with heart health. “It’s important to note that it may not be the best diet for everyone, though,” says Yates.
With that in mind, Yates says you should always consult your healthcare provider about starting a new diet. It’s also a good idea to reach out to a registered dietician/nutritionist for guidance.
“They are your best ally for creating and setting realistic, safe, and healthy goals for your nutrition,” says Yates.
Mediterranean diet and sleep
With all those potential health benefits, we had to know: Could the Mediterranean diet help you catch more Z’s? Emerging research shows it might just do that.
In a recent review of 17 (mostly) observational studies published in 2022, researchers found a potential link between the Mediterranean diet and increased sleep quality—though there’s still more research needing to be done on this particular topic, shares Yates.
In other words? It likely can’t hurt to see if your sleep improves after adopting the Mediterranean diet—and you can keep a sleep journal to see if you indeed sleep better.
FAQs
What are the benefits of the Mediterranean diet?
As Yates details, benefits include lower LDLs (bad cholesterol) and higher HDLs (good cholesterol), lower blood pressure, reduced risk of colorectal, breast, prostate, pancreas, and endometrial cancer, better glucose regulation, and improved cognition. Emerging research shows the Mediterranean diet may potentially lead to better sleep quality as well.
What are the pros and cons of the Mediterranean diet?
The pros are the health gains you might experience, which can head off diseases down the road. But the big con, which is true of any diet, is that following a strict eating plan may leave you feeling frustrated and can even develop into an eating disorder/disordered eating.
What are the top 10 foods in the Mediterranean diet?
There’s no official top 10 food list for the Mediterranean diet. As Yates notes, “All foods can benefit us in different ways—it just depends on the circumstance.” But in general, foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, beans, nuts, legumes, seeds, herbs, spices, fish, and seafood are tent poles of this way of eating.
Another popular eating plan is the keto diet. Learn how the keto diet impacts health and sleep.