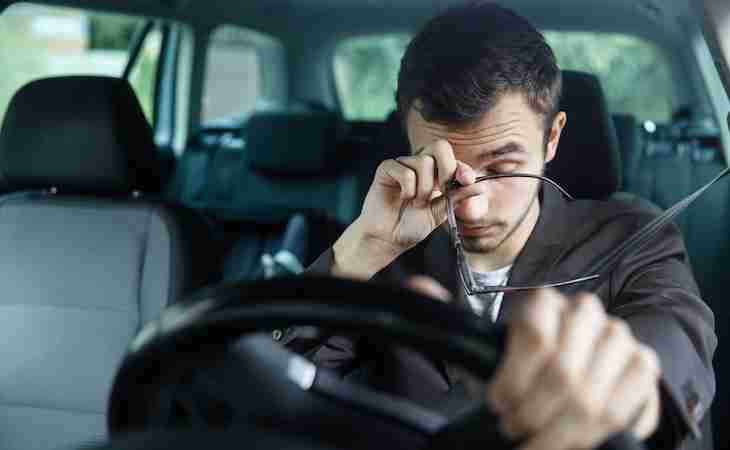
You’re several hours from home, finding yourself feeling tired while driving no matter how much you blast the air conditioning. Several times you’ve found yourself startling because you swerved onto the “rumble strips” on the side of the highway. No matter how much you try to stay awake, you’ve succumbed to drowsy driving.
So what is drowsy driving? It’s driving a vehicle when sleepy—and it’s a dangerous combination. It’s also more common than you might think.
According to a survey report by the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), one in 25 drivers over the age of 18 has fallen asleep while driving in the last 30 days. It’s a statistic that’s alarming for many reasons.
Here, we’ll explore the causes and dangers of drowsy driving along with tips to prevent it.
Why is drowsy driving dangerous?
According to the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA), there were an estimated 91,000 reported crashes that were a direct result of sleepy drivers in 2017. Of those, almost 800 of them resulted in death.
Drowsy driving can affect paying attention to the road and other vehicles. It can also cause you to have a slower reaction time, making an accident more likely if you don’t brake in time.
What are the most common causes of drowsy driving?
Common reasons why you might experience drowsy driving include:
- Sleep deprivation
- Having certain sleep disorders that make falling asleep at the wheel more likely
- Alcohol use
- Taking medications that make you drowsy
- Being the only person in the car
- Driving on rural roads and highways
- Driving during certain hours (drowsy driving crashes tend to happen either in the late afternoon or overnight between 12 a.m. and 6 a.m.)
Who’s most at risk for drowsy driving?
Certain people have an increased risk of driving while drowsy. These include:
- Shift workers: Drivers who work the night shift, such as nurses, are more at risk of driving drowsy. Up to 95% of crashes that involve nurses are because of drowsy driving, according to research.
- Commercial truck drivers: Research has found 13% of crashes were associated with truck driver fatigue.
- Teens and young adults: This age group can be more at risk for drowsy driving because they tend to be more sleep deprived than other age groups.
- People with certain medical conditions: Those who have narcolepsy or untreated sleep apnea are more at risk of driving drowsy and getting in an accident.
What are the warning signs of drowsy driving?
There are some ways to recognize when you may be experiencing drowsy driving and it’s time to pull over for a break. These include:
- Drifting into the other lane or on the shoulder
- Finding your head nodding up and down
- Yawning or blinking frequently
- Feeling like your eyes are tired or drooping
- Trouble focusing
- Missing your exit
- Following the car ahead of you too closely
- Noticing your mind keeps wandering
How do you avoid drowsy driving?
Here are some tips that will help you in a drowsy driving situation, along with how to prevent drowsy driving from happening in the first place.
- Make sure you’re well-rested before heading out on a long car ride.
- Don’t drink alcohol before you drive. This seems obvious when it comes to driving under the influence, but alcohol can make you drowsy as well.
- Avoid driving during the most at-risk hours (late afternoon and midnight to 6 a.m.).
- Avoid driving long distances if you take a medication that can cause drowsiness.
- Pull off the road and take breaks when you find yourself getting sleepy behind the wheel.
- Drive with someone else if possible so you can switch off driving or hold a conversation to keep you alert.
- Don’t try to keep awake if you notice yourself getting drowsy. It’s better to pull over for a break than try to force yourself to stay awake.
- Be wary of relying on caffeine. It’s a short-term solution and may not help you feel fully awake.
- Pull over to a safe spot and take a 20-minute “power nap” if you feel drowsy. They can help you feel more alert and improve your focus, according to the Cleveland Clinic.
FAQs
What’s considered drowsy driving?
Drowsy driving has several warning signs that are important to recognize in order to avoid an accident. Frequent yawning or blinking, head nodding, drifting into another lane, and following another car too closely are all cues that it’s time to pull off the road to rest.
What should drowsy drivers do?
If you find yourself drowsy while driving, pull off at a rest stop or on the side of the road if it’s safe to do so. While turning up the radio, blasting the air conditioner, or singing can make you feel more awake, it’s a temporary solution that can give you false reassurance that you’re awake enough to drive. Taking a 15- to 20-minute nap can help you feel more rested.
What are the consequences of drowsy driving?
If you drive while drowsy, you’re significantly more likely to get in a car accident, injuring yourself and others, or worse. If you’re feeling drowsy, it’s much harder to pay attention to the road and your ability to stop in time or stay in your lane becomes impaired.
How do I stop being drowsy while driving?
Preventing drowsy driving in the first place can help you avoid a potentially dangerous situation down the road (literally). Make sure you get plenty of sleep the night before, avoid alcohol and any medications that could make you sleepy, and don’t try to keep yourself awake while driving if you’re sleepy. It’s better to take frequent breaks than to try to keep yourself awake.
Having trouble sleeping at night? Here are tips to treat insomnia so you can catch the Z’s you need to function at your best.